sacral compression test definition|positive thigh thrust test : commercial Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction is a degenerative condition of the sacroiliac joint resulting in lower back pain. Diagnosis is made clinically with pain just inferior to the posterior superior iliac spine that is made worse with hip . WEBDescription: Mia Dior is a hot babe with a big, gorgeous booty and long flowing red hair. She’s pretty and she’s pissed with her roommate who had an all-night fuckfest with her .
{plog:ftitle_list}
The latest tweets from @idolfap
tests for sacroiliac joint dysfunction
Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction is a degenerative condition of the sacroiliac joint resulting in lower back pain. Diagnosis is made clinically with pain just inferior to the posterior superior iliac spine that is made worse with hip . The Sacroiliac Compression Test is a diagnostic maneuver used to assess sacroiliac joint dysfunction. Evaluate pain and reproduction of symptoms during specific compression movements for improved sacroiliac .
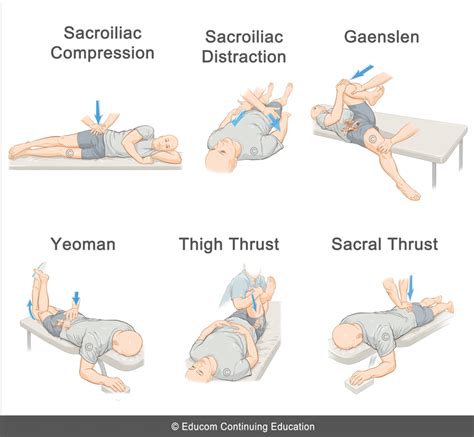
Use the clinical decision rule of at least three out of five positive provocation tests (Gaenslen, thigh thrust, distraction, compression, and sacral thrust) to assist in diagnosing SI joint .
types of hardness testing machine
Sacroiliac joint dysfunction is a term used to describe the pain of the sacroiliac joint (SI joint). It is usually caused by abnormal motion (i.e. hyper- or hypo-mobile) or malalignment of the sacroiliac joint.A.T. Still University School of Osteopathic Medicine in Arizona. Learning Objectives. Review the following diagnostic and treatment techniques related to sacral somatic dysfunction:A clinical test used to identify pain of sacroiliac origin, which consists of placing vertical pressure on the hip of a patient lying on his or her side to spread the anterior superior iliac .While attempting to rule out other causes of low back pain, provocation tests such as FABRE, distraction, thigh thrust, sacral compression, Gaenslen’s, and sacral thrust can be a useful .
Gaenslen's Test (Gaenslen's maneuver) is one of the five provocation tests that can be used to detect musculoskeletal abnormalities and primary-chronic inflammation of the lumbar . While no single physical exam maneuver is diagnostic, a combination of specific findings and provocative tests can be essential in determining SIJ disorders. Specific physical exam provocative tests for SIJ .
Sacroiliac (SI) joint injury is a common cause of low back pain. Posterior pelvic joint pain a common name for SI joint dysfunction. The spine and pelvis are connected by the sacroiliac joint. The SI joint lies between the iliac's articular surface and the sacral auricular surface. When an injury occurs to the SI joint, patients often experience significant pain in their . Oblique or transverse ramus fracture and ipsilateral anterior sacral ala compression fracture. LC II. Rami fracture and ipsilateral posterior ilium fracture dislocation (crescent fracture). . test stability by placing gentle .
The sacral plexus branches into smaller nerves within the pelvis. Some of the nerves remain the pelvis and some extend down the leg. Some nerves of the sacral plexus exit the pelvis through the greater sciatic .The sacral spine consists of five segments, S1 - S5, that together affect nerve communication to the lower portion of the body. It is important to understand that the spinal cord does not extend beyond the lumbar spine. L2 is the lowest vertebral segment that contains spinal cord. After that point, nerve roots exit each of the remaining .The side of the positive seated flexion test identifies the dysfunctional side. Sacral torsions encompass anterior (L on L / R on R) or posterior (L on R / R on L) torsion dysfunctions of the sacrum. With these diagnoses, the deep sacral sulcus and posterior / inferior ILA will be on the opposite side. The oblique axis will occur on the side .While 1 positive test raises suspicion, 3 or more positive tests would indicate the SI joint as a pain generator. The Laslett study indicates that 3 or more positive provocative tests give 91% sensitivity and 78% specificity.1 The Szadek study indicated the thigh thrust and the compression tests both have good singular diagnostic validity.2
The pelvic ring consists of the sacrum and 2 innominate bones, each comprising an ilium, ischium, and pubis. The bony anatomy of the ring lacks inherent stability, underscoring the essential role of strong ligamentous attachments in maintaining its structure. Displacement of the pelvic ring necessitates disruption in at least 2 sites. Pelvic ring injuries encompass a .SacroIliac compression test- reproduction of pain after applying pressure downward on the superior aspect of the iliac crest. Gaenslen test- reproduction of pain after having the patient flex the hip on the unaffected side and then dangle the affected leg off the examining table. Pressure is then directed downward on the leg to extend further .
Compression Test. When performing the Compression Test (Figure 5), the patient lies in the lateral decubitus position, with the affected side up, and facing away from the examiner, who applies a downward pressure to the ipsilateral iliac crest and anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS). The test is considered positive if the patient feels pain in .
Sacral compression test; Downwards pressure test; Sacral spring test; Technique [edit | edit source] With the patient prone, the examiner applies an anteriorly directed pressure over the sacrum. One hand is placed directly on the sacrum and is being reinforced by the other hand. The purpose is to apply an anterior shear force to both sacroiliac .
The test is based on stretching of the nerves in the spine. Crossed Straight Leg Raise Test (Crossed Lasègue test): A test for the containment and exclusion of lumbar radiculopathy. For the cross straight leg raising test a pooled sensitivity was 0.29 (95% CI 0.24-0.34), pooled specificity was 0.88 (95% CI 0.86-0.90) (LOE 1A). The test is . Sacral fractures are common pelvic ring injuries that are under-diagnosed and often associated with neurologic compromise. . test pelvic ring stability by internally and externally rotating iliac wings. palpate for subcutaneous fluid mass indicative of lumbosacral fascial degloving .The FABER test is used to identify the presence of hip pathology by attempting to reproduce pain in the hip, lumbar spine or sacroiliac region. The test is a passive screening tool for musculoskeletal pathologies, such as hip, lumbar spine, or sacroiliac joint dysfunction, or an iliopsoas spasm. The lumbosacral (LS) plexus is a network of nerves formed by the anterior rami of the lumbar and sacral spinal cord. LS plexopathy is an injury to the nerves in the lumbar and/or sacral plexus. LS plexopathy is not an uncommon condition but can be difficult to diagnose and manage.[1] However, it is far less common than brachial plexopathy. Patients with LS .
Purpose [edit | edit source]. The Spurling's test (also known as Maximal Cervical Compression Test and Foraminal Compression Test) is used during a musculoskeletal assessment of the cervical spine when looking for cervical nerve root compression causing Cervical Radiculopathy.. Technique [edit | edit source]. There are different ways described in the literature to perform .The seated flexion test is used to detect sacroiliac joint (SIJ) dysfunction. SIJ dysfunction can be a source of pain in the lower back and buttocks.[1] Toggle navigation. p Physiopedia; p Physiopedia . The test is negative if the movement of the PSISs was symmetrical or positive if one side moved more than the other in the cephalic and/or .The sacrum is a triangular bone formed by 5 vertebral segments. It is broader on the superior side than on the inferior, and broader on the anterior side than on the posterior side, allowing the sacrum to resist shearing from vertical .
The expanded definition for SPD is particularly significant for definite diagnosis and prevention of missing diagnosis, based on which the 301SPD classification criteria can more systemically guide the clinical treatment of SPD, increase the treatment efficacy, and reduce surgical trauma. . 6 patients used sacroiliac compression screws, 3 .There's no single test that can definitively diagnose sacroiliitis. The diagnosis typically involves a combination of physical exams, imaging tests, and blood tests. . Sacral thrust test. The patient lies on their stomach with the clinician placing both hands above the tailbone and applying controlled force to the joints. Pain in the SI joint .
inferolateral to the posterior superior iliac spine. While attempting to rule out other causes of low back pain, provocation tests such as FABRE, distraction, thigh thrust, sacral compression, Gaenslen’s, and sacral thrust can be a useful diagnostic tool for the diagnosis of sacroiliac joint pain. Although recently, the provocation tests’ validity has been challenged. Currently, the most . Dr. Ebraheim’s educational animated video describes the sacral sparing test for spinal cord injury.Sacral sparing tests can be used to indicate the presence .
The sacral vertebrae—also called the sacral spine—consists of five sacral vertebrae bones. These bones fuse together to form the sacrum, the shield-shaped bony structure located at the base of the lumbar vertebrae (the five cylindrical bones forming the spine of the lower bank) and connected to the pelvis. The sacral vertebrae are represented by .The squish test is performed with the patient in a supine position and the anterior-superior iliac spines are palpated. If pain is evoked the test is positive. The results of neurological examination are often normal. Nerve root compression is uncommon but it may cause sphincter dysfunction and lower-limb paresthesias. Laboratory findings
sacroiliac compression test A clinical test used to identify pain of sacroiliac origin, which consists of placing vertical pressure on the hip of a patient lying on his or her side to spread the anterior superior iliac spines (ASIS).
The index test of interest was a pain provocation test in the form of a cluster of pain provocation tests (eg, a combination of the distraction test, compression test, thigh thrust test, Gaenslen test, and sacral thrust test). 20 The reference standard was the use of intra-articular local anesthetic blocks for SIJ pain, according to the . The lumbosacral joint (L5-S1) is a joint in the spinal column between the last vertebra of the lumbar region and the first vertebra of the sacral region. At this point, there is a shift in the curvature of the vertebral column from a forward curvature in the lumbar region to a backward curvature in the sacral section of the spinal column.Introduction. In the realm of pain management, few conditions are as complex and challenging as S1 nerve root compression. This condition often arises from a variety of causes, including herniated or bulging discs in the lower spine, spinal stenosis (narrowing of the spinal canal), spondylolisthesis (slippage of one vertebra over another), degenerative disc disease, and in .

types of hardness testing methods pdf
The latest tweets from @pucconheira
sacral compression test definition|positive thigh thrust test